Reimbursement fast facts: oxygen concentrators
Oxygen concentrators are medical devices that concentrate the oxygen in room air and delivers it to patients who have
significant hypoxemia. Oxygen concentrators may be categorized by whether they are portable or stationary.
Oxygen billing criteria
Oxygen equipment is covered by Medicare for patients with
significant hypoxemia who meet the medical documentation,
laboratory evidence and health conditions specified in the
Medicare national and local coverage determination policies.
Conditions for which oxygen therapy may be covered
include severe lung diseases (e.g. COPD, cystic fibrosis
and bronchiectasis), as well as hypoxia-related symptoms
expected to improve with oxygen therapy (e.g. pulmonary
hypertension, recurring congestive heart failure due to
chronic cor pulmonale, erythrocythemia and nocturnal
restlessness).
Coverage is also contingent upon documentation of a
qualified blood gas study (oximetry test or arterial blood gas
test) that meets the oxygen group coverage criteria (see
next page).
Coverage criteria
Home oxygen therapy is reasonable and necessary only if all
of the following conditions are met:
1. The treating physician has determined that the patient has a
severe lung disease or hypoxia-related symptoms that might
be expected to improve with oxygen therapy, and
2. The patient’s blood gas study meets the criteria stated
below, and
3. The qualifying blood gas study was performed by a
physician, qualified provider or supplier of laboratory
services, and
4. The qualifying blood gas study was obtained under the
following conditions:
• If the qualifying blood gas study was performed during an
inpatient hospital stay, the reported test must be the one
obtained closest to, but no earlier than, two days prior to
the hospital discharge date, or
• If the qualifying blood gas study was performed outside
of an inpatient hospital stay, the reported test must
be performed while the patient is in a chronic stable
state (i.e. not during a period of acute illness or an
exacerbation of their underlying disease) and
5. Alternative treatment measures have been tried or
considered and deemed clinically ineffective.
In this policy, the term “blood gas study” (BGS) refers to
either an oximetry or arterial blood gas (ABG) test.
Understanding Medicare coding and coverage
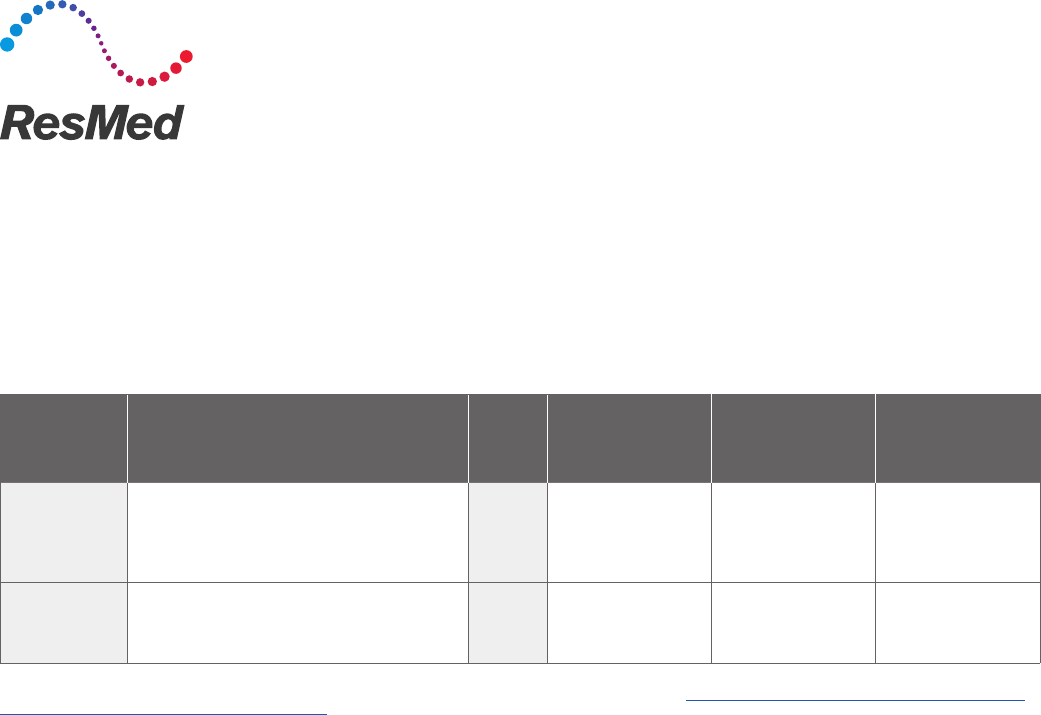
Device Description
HCPCS
Code
Medicare Jan 2019
former Competitive
Bid Area rate*
ceiling - floor
Medicare Jan 2019
non-CBA
non-rural rate*
ceiling - floor
Medicare Jan 2019
non-CBA
rural rate*
Oxygen
concentrator
Oxygen concentrator
Single delivery port, capable of delivering
85% or greater oxygen concentration at
the prescribed flow rate
E1390 $86.24 - $65.44 $134.71 - $68.99 $134.71
Portable
oxygen
concentrator
Portable oxygen concentrator, rental E1392 $39.36 - $31.98 $44.32 - $33.84 $44.32
*Oxygen reimbursement is a bundled payment. All options, supplies and accessories are considered included in the monthly rental payment for oxygen equipment.
1
Non-CBA non-rural rate includes the non-contiguous (Alaska, Hawaii and United
States territories) rates. CMS DME19-A January 2019 DMEPOS fee schedules

Below are documentation requirements for:
Supporting initial oxygen medical necessity:
• Dispensing order
• Detailed Written Order (DWO) or Certificate of Medical
Necessity (CMN) if it contains the same information as
required in a DWO
2
• Medical records
1
that support the patient meets the
Local Coverage Determination (LCD) coverage and
payment requirements:
- Patient Authorization
- Continued Use
- Continued Need
• Proof of Delivery
Ongoing coverage:
• Recertification CMN
- Group I: 12 months after initial certification with most
recent BGS performed prior to 13th month of therapy
- Group II: three months after initial certification with
most recent BGS performed between 61st and 90th
day following initial certification
• Medical records documenting that the patient was
seen and re-evaluated by the treating physician within
90 days prior to the date of any recertification.
3
• Continued medical need for the equipment,
accessories and/or supplies is verified by either:
- A properly completed CMN with a specified length of
need, or
- A recent refill order by the treating physician, or
- A recent change in prescription, or
- Timely documentation in the patient’s medical record
specifying item usage
Portable oxygen systems:
• Medical records supporting that the patient is mobile
within the home and the qualifying blood gas study
was performed at rest (awake) or during exercise.
Liter flows greater than 4 LPM:
• A copy of the blood gas study showing blood gas
levels in the Group I or Group II range while the patient
was receiving oxygen at the rate of at least 4 LPM
Medicare’s oxygen coverage criteria divide patients into
three coverage groups (Group I, II and III). Payment is
available for patients whose test results place them in
either Group I or II.
Group I criteria include any of the following:
An ABG at or below 55 mm Hg or oxygen saturation (SAT) at or
below 88% and is performed:
1. At rest, or
2. During exercise (three tests), or
3. During sleep for at least five minutes, or
4. During sleep with signs of hypoxemia and test shows a
decrease in the ABG of more than 10 mm Hg or a decrease in
the SAT of more than 5% from baseline for at least five minutes.
Initial coverage for patients meeting Group I criteria is limited to
12 months or the physician-specified length of need, whichever is
shorter. (Refer to the “documentation requirements” section for
information on recertification.)
Group II criteria include:
1. An ABG between 56–59 mm Hg or SAT at 89%
a. Follows same testing requirements as Group I, and
2. Patient has one of the following conditions:
a. Dependent edema suggesting congestive heart failure, or
b. Pulmonary hypertension or cor pulmonale, or
c. Erythrocythemia with a hematocrit greater than 56%
Initial coverage for patients meeting Group II criteria is
limited to three months or the physician-specified length of
need, whichever is shorter. (Refer to the “documentation
requirements” section for information on recertification.)
Group III includes patients with arterial PO2 levels at or above
60 mm Hg or arterial blood oxygen saturations at or above 90%.
Group III patients are generally not covered.
2
Refer to the Oxygen
and Oxygen Equipment Local Coverage Determination policy for
complete Group I, II and II coverage criteria.
Q: Can oximetry data from ResMed ApneaLink Air™ or
ResMed AirView™ (when an oximeter is connected to
a positive airway pressure device) be used to qualify a
patient for home oxygen?
No, patients with known or suspected OSA must
be tested in-person, either via an overnight titration
polysomnogram or via an awake in-person oximetry test.
All awake oximetry results must be obtained in-person
by a qualified medical professional with the exception of
overnight oximetry. Unsupervised or remotely supervised
awake home testing does not qualify as a valid test. For
patients with OSA, a qualifying oxygen saturation test may
only occur during a titration polysomnographic study or
during an in-person, supervised, awake test.
1
Q & A
Q: When oxygen qualification testing is obtained from a
titration polysomnogram, is portable oxygen covered?
No, as with overnight oximetry, only stationary oxygen may
be justified based on titration polysomnography (PSG).
4
Q: What testing is required for patients with suspected
or known obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) to qualify for
home oxygen?
During qualification testing, the patient must be in a chronic
stable state, meaning obstructions need to be resolved
during testing. Therefore, an OSA patient must qualify
while they are awake or during a titration PSG conducted
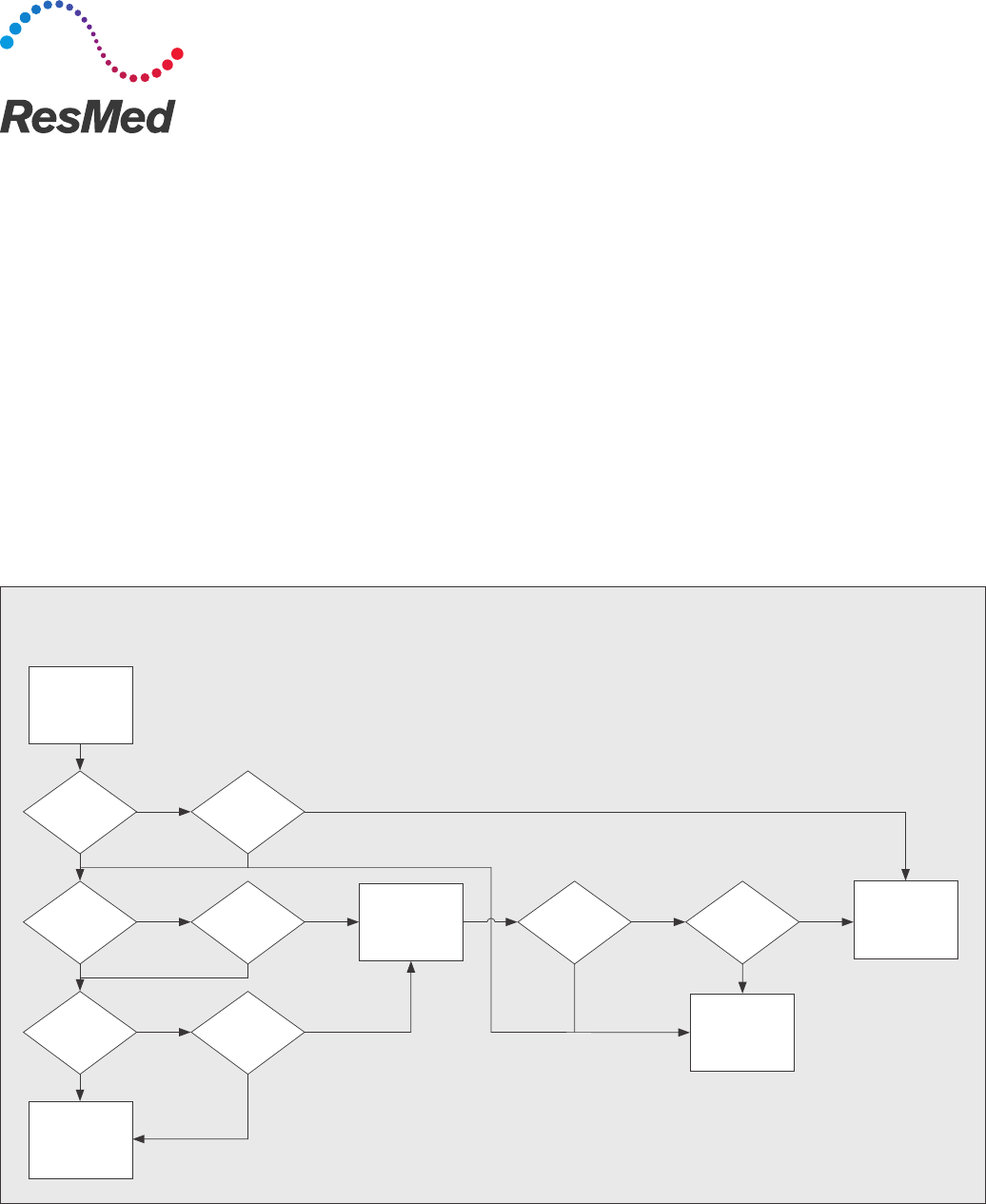
at sleep. CGS has provided a helpful decision tree to
illustrate this point (see chart below).
4
Testing required for home oxygen qualification in patients with known or suspected OSA
All testing must meet the requirements set out in the Medicare
LCDs for positive airway pressure (PAP) devices and oxygen
and oxygen equipment
Known or
suspected
OSA
PAP covered
PAP not covered
Home oxygen
covered
Home oxygen
not covered
Oximetry while
awake?
Y
Y
Y Y
Y Y Y
Y
nn
nn n n
nn
HST done? Titration PSG
PSG done
Qualifying
result?
HST
diagnostic?
Hypoxic
after titration
PSG
diagnostic?
As of Nov 2013
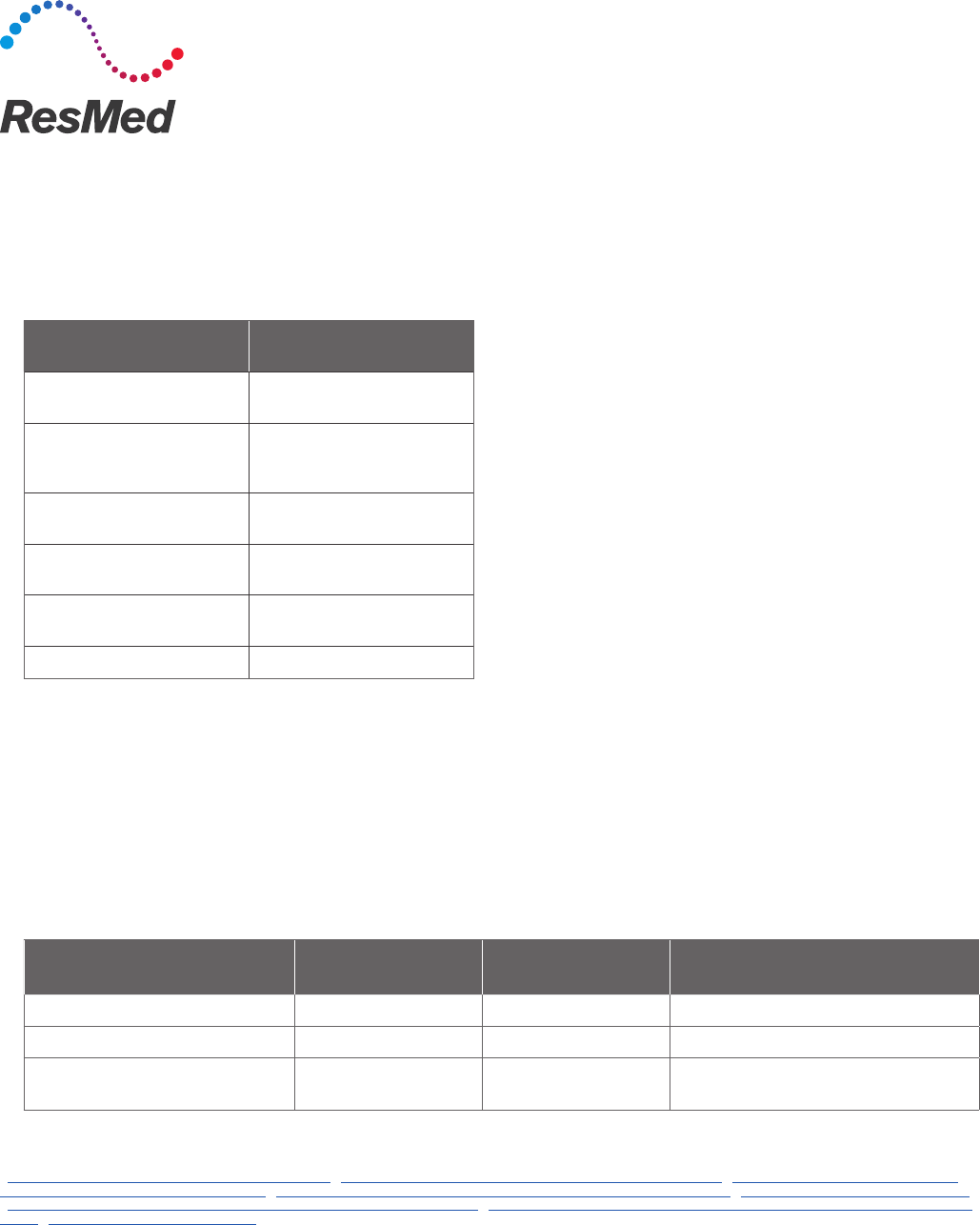
Description
At rest
(no liter flow change)
Average of day &
nighttime use
Stationary payment is
Stationary O2 is < 1 LPM QE QA reduced 50%
Stationary O2 is > 4 LPM QG QR increased 50%
Stationary O2 is > 4 LPM
and portable O2 is prescribed*
QF QB increased 50% or add-on portable fee
schedule (whichever is higher)
Distributed by ResMed Corp, 9001 Spectrum Center Boulevard, San Diego, CA 92123 USA +1 858 836 5000 or 1 800 424 0737 (toll free). See ResMed.com for other ResMed locations worldwide. AirView and ApneaLink Air are trademarks and/or
registered trademarks of the ReMed family of companies. Specifications may change without notice. For patent and other intellectual property information, see ResMed.com/ip. © 2019 ResMed. 1019395/4 2019-01
The reimbursement information is being provided on an “as is” basis with no express or implied warranty of any kind and should be used solely for your internal informational purposes only. The information does not constitute professional or
legal advice on reimbursement and should be used at your sole liability and discretion. All coding, coverage policies and reimbursement information are subject to change without notice. ResMed does not represent or warrant that any of the
information being provided is true or correct and you agree to hold ResMed harmless in the event of any loss, damage, liabilities or claims arising from the use of the reimbursement information provided to you. Before filing any claims, it is the
provider’s sole responsibility to verify current requirements and policies with the payor.
Q: What oxygen equipment is billable for contents post
36-month cap?
Only gaseous and liquid tank systems are eligible for post
36-month cap content billing. Oxygen concentrators and
transfilling equipment are not eligible for contents payment.
5
Q: Do all oxygen items require a written order prior to
delivery (WOPD)?
No, the following items do not require a WOPD: oxygen
concentrators (E1390 or E1391), portable oxygen
concentrators (E1392) and portable gaseous equipment
(K0738). While a WOPD is not required for these specific
items, a detailed written order (DWO) is required prior to
billing for other oxygen equipment.
6
Q: What maintenance and servicing fees are applicable to
oxygen concentrators?
A maintenance and servicing fee of ~$72 is paid every
six months, either beginning: 1) six months after the 36th
paid rental month, or 2) when the item is no longer covered
under the supplier’s or manufacturer’s warranty (whichever is
later). Only one maintenance and servicing payment can be
made for patients using both stationary (E1390) and portable
oxygen concentrators (E1392). Note: Neither patient-owned
gaseous nor liquid oxygen equipment (stationary or portable)
is eligible for maintenance and servicing payments. Service
must be performed and documented via a service ticket to bill
for maintenance fees.
7
Oxygen equipment
furnished in month 36
Monthly contents payment
after the stationary cap
Oxygen Concentrator (E1390
or E1391)
None
Portable Gaseous or Liquid
Transfilling Equipment (K0738,
E1392 or E0433)
None
E0424 Stationary Gaseous
System
E0441 Stationary Gaseous
Contents
E0439 Stationary Liquid
System
E0442 Stationary Liquid
Contents
E0431 Portable Gaseous
System
E0443 Portable Gaseous
Contents
E0434 Portable Liquid System E0444 Portable Liquid Contents
1 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Oxygen and Oxygen Equipment (L33797) 2 Oxygen and Oxygen Equipment Local Coverage Determination (LCD) and Policy Article [PDF] 3 Oxygen and Oxygen Equipment Beneficiaries Meeting
Group II criteria Documentation Checklist; CGS August 10, 2017 4 Frequently Asked Questions: Oxygen Use in Beneficiaries with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (November 22, 2013) 5 MLN Matters (MM7416) Payment for Oxygen Contents
6 Local Coverage Article: Standard Documentation Requirements for All Claims Submitted to DME MACs (A55426) 7 Calendar Year (CY) 2019 Update for Durable Medical Equipment, Prosthetics, Orthotics and Supplies (DMEPOS) Fee
Schedule 8 Revised and New Modifiers for Oxygen Flow Rate
ResMed.com/Reimbursement
Q: How does payment change for patients who need more than 4 LPM or less than 1 LPM?
This depends on several factors and the modifier being used. Selecting the appropriate modifier depends on the liter flow,
whether the stationary oxygen liter flow differs between day and nighttime use, and whether portable oxygen is prescribed.
The monthly payment for stationary oxygen is reduced by 50% when the stationary at rest liter flow is less than 1 LPM
and increased by 50% when the at rest liter flow is greater than 4 LPM. When portable oxygen is also prescribed, payment
is increased by the higher of 50% of the monthly stationary payment amount or the fee schedule amount for the portable
oxygen add-on. When the stationary liter flow rates differ between day and nighttime use, Medicare expects suppliers to
average the liter flow prior to assessing payment eligibility for the volume adjustment.
8
The following table identifies the modifier to use based upon the situation.
*Note: When billing for higher liter flow reimbursement, separate payment for portable oxygen is not allowed.
8
